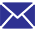
FRP pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that produces strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant profiles. This article explains how the process works, its advantages, and how it compares to other FRP fabrication techniques, helping you choose the right material for your project.
Cable Ladder vs. Cable Tray: Choosing the Right Cable Management System
02 Sep 2024
Cable Management: Top Tips for Organizing Wires
Cable Management: Top Tips for Organizing Wires
- Cable Ladder vs. Cable Tray: Key Differences & Applications
- What Are Cable Ladders and Cable Trays?
- Common Applications of Cable Ladders and Cable Trays
- Why Choose Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Over Aluminum?
- When and Where to Use Cable Ladders and Trays
- Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Cable Management
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the primary difference between a cable ladder and a cable tray?
- Why is Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) preferred over aluminum in cable management?
- Can cable trays support heavy cables?
- Where are cable ladders typically installed?
- Are there specific environments where cable trays should not be used?
Cable Ladder vs. Cable Tray: Key Differences & Applications
In today's complex electrical and telecommunications infrastructure, proper cable management is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of the system. Two of the most common cable management systems are Cable Ladders and Cable Trays. These systems are essential for organizing and supporting cables in various environments, but they have distinct differences that make them suitable for different applications. In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive deep into what sets cable ladders apart from cable trays, explore their common uses, and discuss why Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) is often the preferred material over more traditional options like aluminum.
What Are Cable Ladders and Cable Trays?
 Cable Ladder
Cable Ladder
A Cable Ladder, often known as a ladder tray or cable runway, is a simple yet highly effective cable management system. It consists of two side rails connected by rungs, which are usually perforated to allow for easy fastening of cables using ties or cleats. This open design makes it particularly well-suited for supporting heavy cables, cable bundles, and even pipes over long spans. The ability of the rungs to allow cables to enter and exit freely along the span, combined with the excellent airflow provided by the open structure, helps prevent overheating - a critical consideration in environments where large amounts of power are being transmitted.
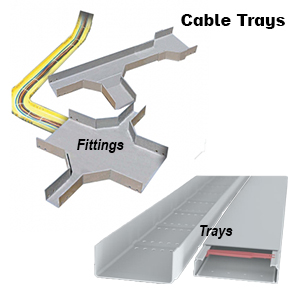 Cable Tray
Cable Tray
On the other hand, a Cable Tray, sometimes known as a trough or ventilated cable tray, is a cable management system that consists of a single sheet of material - often slotted or perforated. Cable trays are designed to support lighter electrical and instrumentation cables, offering a continuous surface that prevents cables from drooping, which could potentially damage the circuit's performance. The design also helps reduce electromagnetic interference, making it an excellent choice for environments where this is a concern. Moreover, the tray's slots or perforations enable water drainage and ventilation, further enhancing its performance in various settings.
|
Feature |
FRP Cable Ladder |
FRP Cable Tray |
|---|---|---|
|
Other Names |
Ladder tray, cable runway |
Trough, ventilated cable tray |
|
Design |
Simple structure with side rails and perforated rungs |
Single FRP sheet with slotted patterns |
|
Material |
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
|
Load Capacity |
High; supports heavy cables, bundles, and pipes |
Moderate; suited for lighter electrical cables and tubing |
|
Flexibility |
Rigid; ideal for long, straight runs; adaptable with fittings |
Highly flexible; fits confined spaces, allows future adjustments |
|
Airflow & Ventilation |
Excellent airflow; prevents cable overheating |
Perforations enable drainage and ventilation |
|
Cable Management |
Cables can enter/exit anywhere along the span |
Prevents cable drooping; aesthetically organizes cables |
|
Accessibility |
Easy to inspect, modify, and maintain |
Keeps cables hidden yet organized; visually appealing |
|
Protection Options |
Covers can be added for protection against UV, weather, and vandalism |
Covers can be added for enhanced protection |
Common Applications of Cable Ladders and Cable Trays
Both cable ladders and cable trays have specific applications where they excel, depending on the type of cables being managed and the environment in which they are installed.
Cable Ladder: Industrial Plants and Telecommunications Infrastructure
Cable ladders are commonly used in industrial plants, where they are required to support heavy-duty cables over long distances. Their robust design makes them ideal for environments like power plants, oil and gas facilities, and large manufacturing operations where significant cable loads need to be managed efficiently. Additionally, cable ladders are often found in telecommunications infrastructure, where their open design allows for easy installation, maintenance, and future modifications. This is particularly important in large-scale telecom setups, where the need to add or remove cables frequently is common.
Cable Trays: Commercial Buildings and Data Centers
In contrast, cable trays are often preferred in spaces where aesthetic considerations are important, commercial buildings for instance. The ability of cable trays to neatly organize and conceal cables makes them an excellent choice in environments without paneled ceilings. Data centers also commonly use cable trays to support numerous smaller cables, providing an organized and protected environment for critical data transmission pathways. In such settings, the reduction of electromagnetic interference offered by the solid bottom of a cable tray is a significant advantage.
Why Choose Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Over Aluminum?
While aluminum is often seen as a cost-effective option for cable management systems, Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) offers several superior benefits that make it the material of choice for many critical applications.
Corrosion Resistance and Non-Conductivity
One of the most significant advantages of FRP over aluminum is its corrosion resistance. FRP is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals and environmental conditions, making it ideal for use in harsh environments such as chemical plants, offshore platforms, and wastewater treatment facilities. In these settings, aluminum can corrode over time, leading to structural failure and increased maintenance costs. FRP's non-conductive properties also enhance safety by reducing the risk of electrical hazards, a crucial consideration in environments where electrical insulation is vital.
Lightweight Yet Strong and UV Resistance
FRP is not only corrosion-resistant but also lightweight and strong, providing a durable solution that does not add significant weight to the installation. This can be particularly important in installations where structural load is a concern. Additionally, FRP offers UV resistance, meaning it won't degrade when exposed to sunlight over long periods. This makes it a reliable choice for outdoor installations, where prolonged exposure to the elements is unavoidable.
When and Where to Use Cable Ladders and Trays
Choosing between a cable ladder and a cable tray depends on the specific needs of your installation, including the type of cables, the environments, and the required support.
Locations Suited for Cable Ladders
-
Long, Straight Cable Runs - Cable ladders are best suited for long, straight cable runs, where their rigid structure provides excellent support over extended distances. This makes them ideal for use in industrial settings where large, heavy cables need to be supported without sagging.
-
Harsh Environments - In harsh environments, such as offshore platforms or chemical plants, where exposure to chemicals, saltwater, or extreme temperatures is common, the corrosion resistance of FRP cable ladders makes them the best choice.
-
High Cable Loads - When supporting heavy cable loads, especially in power generation or large-scale telecommunications installations, the robust design of a cable ladder ensures reliable performance.
Locations Suited for Cable Trays
-
Complex Layouts - Cable trays are ideal for installations that require numerous changes in direction or level. Their flexible design, along with cable management accessories such as cable clips, allows them to be easily adapted to fit into confined spaces, making them a good choice for complex layouts in buildings or data centers.
-
Aesthetic Requirements - In commercial or public spaces, where the appearance of the cable management system matters, cable trays provide a neat and organized solution. Their ability to conceal cables makes them a preferred option in environments like offices or shopping centers, where a clean look is important.
-
Light to Moderate Cable Loads - Cable trays are suitable for installations where the cables are lighter and the load is more evenly distributed. This includes applications like data centers, where many small cables need to be supported in a highly organized manner.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Cable Management
When it comes to cable management, both Cable Ladders and Cable Trays offer distinct advantages depending on the needs of your project. While aluminum might seem like an economical choice, the long-term benefits of Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) - including superior corrosion resistance, non-conductivity, and durability - make it the preferred material for many critical applications. By understanding the differences between these systems and their common applications, you can make an informed decision that will ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your cable management system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary difference between a cable ladder and a cable tray?
A cable ladder is designed for heavy cables and long spans with minimal direction changes, while a cable tray is better suited for lighter cables and more complex layouts.
Why is Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) preferred over aluminum in cable management?
FRP offers superior corrosion resistance, non-conductivity, and UV resistance, making it more durable and safer for use in harsh environments compared to aluminum.
Can cable trays support heavy cables?
Cable trays are generally designed for lighter to moderate cable loads. For heavy cables, cable ladders are recommended due to their robust design.
Where are cable ladders typically installed?
Cable ladders are commonly used in industrial plants, telecommunications infrastructure, and harsh environments like offshore platforms where heavy-duty cables need support.
Are there specific environments or options where cable trays should not be used?
Cable trays may not be ideal in environments with extremely high cable loads or where long, uninterrupted spans are required, as they are better suited for light to moderate cables and complex layouts.
Disclaimer:-
The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability concerning the information contained herein. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. This website may contain links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user, or browser; which we do not warrant, recommend, endorse, or assume liability for the contents of the third-party sites.
Keep in touch with us should you be keen on receiving timely updates from us
- Website - https://www.muifatt.com.my/home/
- Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/muifattmarketing
- Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/muifattmarketing/
- Google - https://goo.gl/maps/WxVY13gNcaRTS7Jp6
- Youtube - http://www.youtube.com/@MuiFattMarketing
- TikTok - https://www.tiktok.com/@muifattmarketing
- LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/mui-fatt-marketing-sdn-bhd-
- Linktree - https://linktr.ee/muifattmarketing
- Shopee - https://www.shopee.com.my/muifattmarketing
- Lazada - https://www.lazada.com.my/shop/mui-fatt-marketing
Recent Blog
The Ultimate Guide to Locking Mechanisms for FRP Molded Grating
Understanding the right locking method for FRP molded grating is crucial for safety and durability. Learn about M clips, J clips, C clips, and disk plates, along with installation recommendations to ensure a secure and stable grating system.
Enhancing Solar Panel Fixing Structures with FRP Lamination: A Corrosion Barrier Solution
An expert look at how FRP lamination acts as a corrosion barrier for solar panel fixing structures, offering advanced protection and sustainability benefits.
Steel Fixing Structures in Solar Panel Installations: Corrosion Challenges and Alternative Materials
An in-depth look at the corrosion challenges faced by steel solar panel fixing structures and alternative materials that offer enhanced durability and sustainability.
The Essential Guide to Kickplates: Safety, Style & Compliance
Learn why kickplates matter for safety, style, and compliance. Discover how they improve accessibility and meet building code requirements.
The Costly Mistake of Using Unsuitable Resin for FRP Tanks
Explore the risks of unsuitable resins for FRP wastewater tanks, including a real-life example of NaOH corrosion. Learn how to avoid costly failures.
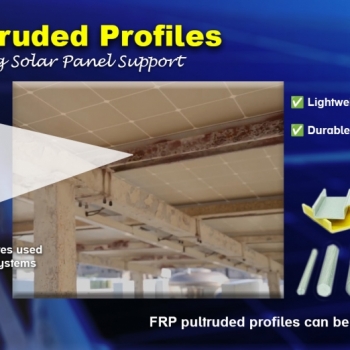
Mastering the FRP Hand Lay-Up Process: Methods, Benefits, Sustainability
Discover the FRP hand lay-up manufacturing process, its importance, differences from other methods, and how it aligns with your custom project needs.
Transform DIY Projects with FRP Pultruded Profiles
Explore the versatility of FRP pultruded profiles and how they can elevate your DIY landscaping projects. Get inspired by Mui Fatt's successful applications and learn how to create custom solutions for small- to larger-scale projects.