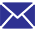
FRP pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that produces strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant profiles. This article explains how the process works, its advantages, and how it compares to other FRP fabrication techniques, helping you choose the right material for your project.
Enhancing Solar Panel Fixing Structures with FRP Lamination: A Corrosion Barrier Solution
07 Feb 2025
Enhancing Solar Panel Fixing Structures with FRP Lamination: A Corrosion Barrier Solution
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding FRP Lamination
- How FRP Lamination Acts as a Corrosion Barrier
- Application in Solar Panel Fixing Structures
- Sustainability and Lifecycle Considerations
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Key Takeaways
-
Innovative Protection: FRP lamination offers a modern approach to protecting solar panel fixing structures against corrosion.
-
Robust Barrier Properties: The composite layer provides an effective physical barrier, significantly reducing the risk of corrosion.
-
Customizable Solutions: FRP can be tailored to meet specific performance criteria, including thickness, reinforcement orientation, and environmental resistance.
-
Sustainability Benefits: Although primarily petrochemical-based, advancements in FRP technology are enhancing recyclability and reducing environmental impact over the lifecycle.
As the demand for renewable energy continues to surge, the integrity and longevity of solar panel installations become increasingly critical. Traditional steel fixing structures, while strong and cost-effective, suffer from corrosion issues that can compromise their performance over time. To address this, innovative solutions such as Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) lamination have emerged, offering enhanced protection against environmental degradation.
This article explores how FRP lamination serves as an effective corrosion barrier, providing solar panel fixing structures with improved durability and sustainability.
Understanding FRP Lamination
Fiberglass-reinforced Plastic (FRP) lamination involves applying a composite material—composed of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers (such as glass, carbon, or aramid)—directly onto steel structures. This process creates a protective layer that offers several key benefits:
-
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: FRP adds minimal weight while significantly enhancing structural integrity.
-
Customizable Properties: The composition and thickness of the FRP layer can be engineered to suit specific environmental and mechanical requirements.
-
Chemical and Environmental Resistance: The composite layer acts as an effective barrier against moisture, salts, and other corrosive agents.
The FRP lamination process typically involves the following key steps:
-
Surface Preparation
The steel or substrate surface is thoroughly cleaned to remove contaminants such as grease, dirt, or rust. Abrasive blasting or mechanical sanding is commonly used to create a roughened surface, improving adhesion between the substrate and the FPR layer. -
Application of a Primer or Base Layer
A primer of base coat is often applied to the prepared surface to enhance the bonding of the FRP material. This layer acts as an intermediary, ensuring strong adhesion and a uniform application. -
Laying of Reinforcement Fibers
Fibers, such as glass, carbon, or aramid, are carefully placed on the substrate. These fibers are typically available in mats, fabrics, or unidirectional sheets, depending on the specific design requirements. -
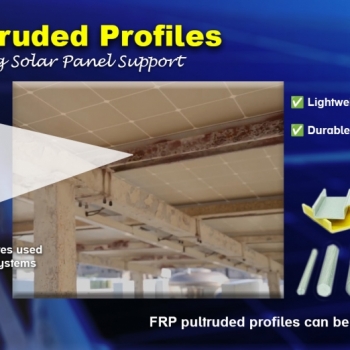
Resin Application
A polymer resin (commonly polyester, epoxy, or vinyl ester) is applied over the reinforcement fibers. The resin acts as matrix, binding the fibers together and forming the composite material. This step may involve hand layup, spray application, or infusion methods, depending on the complexity of the structure. -
Curing
The FRP layer is left to cure, either at room temperature or with the application of heat, depending on the resin type. During curing, the resin hardens, forming a durable, rigid layer with high mechanical and chemical resistance. -
Inspection and Finishing
Once cured, the laminated structure is inspected for defects such as air bubbles, uneven surfaces, or delamination. Any imperfections are corrected, and a final topcoat may be applied for added UV resistance or aesthetic purposes.
This process ensures that the FRP layer adheres seamlessly to the steel structure, creating a robust barrier against corrosion and environmental degradation.
How FRP Lamination Acts as a Corrosion Barrier
FRP lamination protects steel structures through a combination of physical and chemical mechanisms:
-
Physical Barrier: The continuous FRP layer isolates the underlying steel from environmental elements, preventing moisture and corrosive agents from making contact.
-
Enhanced Durability: Unlike traditional coatings that may degrade over time, a well-applied FRP layer maintains its integrity even under harsh conditions.
-
Reduced Maintenance: With improved resistance to corrosion, structures with FRP lamination require less frequent maintenance and repair, reducing overall lifecycle costs.
While FRP lamination is highly effective, it is important to note that its performance depends on proper installation, design, and periodic inspection—especially in areas with high UV exposure or mechanical wear.
Application in Solar Panel Fixing Structures
FRP lamination has proven to be an innovative solution for enhancing the durability of solar panel fixing structures. In practical applications, FRP-coated structures have demonstrated:
-
Extended Lifespan: By minimizing corrosion, FRP extends the service life of solar panel mounting systems.
-
Enhanced Structural Integrity: The added layer improves the overall robustness of the structure, making it more resilient to environmental and mechanical stresses.
-
Ease of Retrofitting: Existing steel structures can often be retrofitted with FRP lamination, providing a cost-effective upgrade without the need for complete replacement.
Sustainability and Lifecycle Considerations
While FRP lamination is primarily based on petrochemical materials, ongoing research is focused on improving its environmental profile. Key sustainability considerations include:
-
Lifecycle Benefits: Reduced maintenance frequency and extended service life can offset the environmental impact associated with the initial production of FRP.
-
Innovative Materials: Advances in bio-based resins and improved recycling methods are making FRP a more sustainable option over time.
-
Environmental Protection: By significantly reducing corrosion and extending the lifespan of structures, FRP lamination contributes to overall resource conservation and waste reduction.
Conclusion
FRP lamination represents a cutting-edge solution for addressing the persistent problem of corrosion in solar panel fixing structures. By serving as a robust physical barrier, FRP not only protects steel components but also enhances the overall durability and sustainability of solar installations.
For professionals in the renewable energy sector, adopting FRP lamination can lead to lower maintenance costs, improved safety, and longer-lasting structures. As the technology continues to evolve—with a focus on eco-friendly materials and improved recyclability—FRP lamination is poised to become a cornerstone of modern solar panel infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is FRP lamination and how does it work?
FRP lamination involves applying a composite layer made of a polymer matrix and reinforcing fibers to steel structures, creating a physical barrier that prevents corrosive agents from reaching the metal.
How does FRP compare to traditional corrosion protection methods?
Unlike conventional coatings, FRP offers a more durable, customizable, and robust barrier against corrosion, often resulting in lower maintenance and longer service life.
Can existing steel structures be retrofitted with FRP lamination?
Yes, FRP lamination can be applied to existing structures as a retrofit solution, providing enhanced corrosion protection without the need for complete replacement.
What sustainability benefits does FRP offer?
Although based on petrochemical components, FRP lamination reduces maintenance frequency and extends structural lifespan, contributing to resource conservation and lower overall environmental impact.
#FRPlamination #corrosionbarrier #solarpanelstructures #FRPcoating #renewableenergy #solarinfrastructure #compositematerials #durability
Disclaimer:-
The content on this site is for general information and entertainment purposes and does not constitute legal counsel. We strive to keep our information as accurate as possible. However, we make no warranties about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the information contained on this page. You should rely on this information at your own risk. This website may include links to other third-party sites. These links are provided as a convenience to you as a reader, user, or browser only. We make no representation, warranty, or guarantee, nor do we endorse or take responsibility for any of the content of such sites.
Stay in touch with us if you’re interested in hearing from us promptly.
- Website - https://www.muifatt.com.my/home/
- Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/muifattmarketing
- Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/muifattmarketing/
- Google - https://goo.gl/maps/WxVY13gNcaRTS7Jp6
- Youtube - http://www.youtube.com/@MuiFattMarketing
- TikTok - https://www.tiktok.com/@muifattmarketing
- LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/mui-fatt-marketing-sdn-bhd-
- Linktree - https://linktr.ee/muifattmarketing
- Shopee - https://www.shopee.com.my/muifattmarketing
- Lazada - https://www.lazada.com.my/shop/mui-fatt-marketing
Recent Blog
The Ultimate Guide to Locking Mechanisms for FRP Molded Grating
Understanding the right locking method for FRP molded grating is crucial for safety and durability. Learn about M clips, J clips, C clips, and disk plates, along with installation recommendations to ensure a secure and stable grating system.
Steel Fixing Structures in Solar Panel Installations: Corrosion Challenges and Alternative Materials
An in-depth look at the corrosion challenges faced by steel solar panel fixing structures and alternative materials that offer enhanced durability and sustainability.
The Essential Guide to Kickplates: Safety, Style & Compliance
Learn why kickplates matter for safety, style, and compliance. Discover how they improve accessibility and meet building code requirements.
Essential Guidelines for Water & Septic Tanks in Borneo
Understand the regulations and guidelines for water and septic tanks in Borneo, plus compliance with SPAN, IWK, and SIRIM standards in Malaysia.
The Costly Mistake of Using Unsuitable Resin for FRP Tanks
Explore the risks of unsuitable resins for FRP wastewater tanks, including a real-life example of NaOH corrosion. Learn how to avoid costly failures.
Mastering the FRP Hand Lay-Up Process: Methods, Benefits, Sustainability
Discover the FRP hand lay-up manufacturing process, its importance, differences from other methods, and how it aligns with your custom project needs.
Transform DIY Projects with FRP Pultruded Profiles
Explore the versatility of FRP pultruded profiles and how they can elevate your DIY landscaping projects. Get inspired by Mui Fatt's successful applications and learn how to create custom solutions for small- to larger-scale projects.