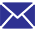
FRP pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that produces strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant profiles. This article explains how the process works, its advantages, and how it compares to other FRP fabrication techniques, helping you choose the right material for your project.
Steel Fixing Structures in Solar Panel Installations: Corrosion Challenges and Alternative Materials
06 Feb 2025
Steel Fixing Structures in Solar Panel Installations: Corrosion Challenges and Alternative Materials
- Key Takeaways
- The Corrosion Challenge in Steel Structures
- Alternative Materials to Steel
- Lifecycle and Sustainability Considerations
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Key Takeaways
-
Corrosion is a Critical Issue: Steel fixing structures for solar panels face significant corrosion challenges in outdoor environments.
-
Economic & Safety Impacts: Corrosion increases maintenance costs, poses safety risks, and shortens the lifespan of installations.
-
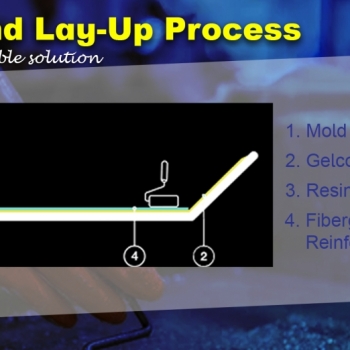
Exploring Alternatives: Materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and composite materials such as Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic offer improved corrosion resistance and longer service life.
-
Sustainability Benefits: Adopting alternative materials can enhance the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of solar panel installations.
Solar panel installations are on the rise worldwide as the demand for renewable energy grows. A critical yet often overlooked component of these systems is the fixing structure—the metal framework that secures the panels. Traditionally, steel is favored for its strength and cost-effectiveness. However, when exposed to outdoor elements, steel is highly prone to corrosion, which can compromise both the integrity and safety of the installation over time.
In this article, we delve into the corrosion challenges inherent in steel-based fixing structures for solar panels and explore alternative materials that offer enhanced durability and sustainability.
The Corrosion Challenge in Steel Structures
 Steel, while robust and versatile, is inherently susceptible to corrosion when exposed to environmental elements such as moisture, salt, and varying temperatures. In solar panel installations, factors like high humidity, coastal salt spray, and temperature fluctuations accelerate the corrosion process. Over time, this degradation can lead to:
Steel, while robust and versatile, is inherently susceptible to corrosion when exposed to environmental elements such as moisture, salt, and varying temperatures. In solar panel installations, factors like high humidity, coastal salt spray, and temperature fluctuations accelerate the corrosion process. Over time, this degradation can lead to:
-
Structural Weakening: Reduced load-bearing capacity and compromised integrity.
-
Increased Maintenance: Frequent repairs and replacements add to the lifecycle cost.
-
Safety Risks: Structural failures may lead to accidents or panel detachment.
The challenges extend beyond structural deterioration and economic costs; they can also have severe safety implications. For instance, a broken/fallen-off solar ground wire—resulting from corrosion or structural failure—can create potentially hazardous situations. Without a proper grounding path, the electrical system is at significant risk:
-
Electrical Shock Risk: Fault currents can travel through a person touching the system, causing severe electric shocks.
-
Equipment Damage: Electrical surges, such as those from lightning strikes or internal faults, may damage critical components in the solar array.
-
System Malfunction: A compromised ground wire can disrupt the electrical system, leading to malfunctions or even a complete shutdown.
In large-scale solar farms, the impact of corrosion on ground wires and fixing structures is magnified, increasing the likelihood of downtime, safety hazards, and costly repairs. The need for continuous maintenance—such as recoating or replacing corroded parts—not only escalates operational costs but also reduces the overall efficiency of the system.
Addressing these issues requires a proactive approach during the design and material selection phases. Environmental conditions should be carefully assessed, and protective measures like advanced coatings or alternative materials with higher corrosion resistance should be prioritized. This holistic strategy ensures the long-term safety, reliability, and efficiency of solar panel installations, minimizing both operational disruptions and risks to personnel.
Understanding these issues is critical for stakeholders who want to ensure long-term reliability and cost efficiency in their solar installations.
Alternative Materials to Steel
Given the inherent challenges of using steel in corrosive environments, several alternative materials have emerged as potential solutions:
| Material | Advantages | Limitations |
Stainless Steel |
|
|
Aluminum |
|
|
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
|
|
Key Takeaways for FRP as a Manufacturer:
-
FRP’s corrosion resistance is unmatched, making it ideal for solar panel structures in highly corrosive environments like coastal areas.
-
While initial costs may seem higher, FRP’s long service life and minimal maintenance deliver superior value over time.
-
As a non-conductive material, FRP is particularly safe for electrical installations, adding to its appeal in renewable energy projects like solar infrastructure.
Lifecycle and Sustainability Considerations
When selecting a material for solar panel fixing structures, it is essential to consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term lifecycle and sustainability. While traditional steel structures may appear cost-effective initially, the expenses associated with frequent maintenance and eventual replacement can be significant. In contrast, alternative materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and composites often offer:
-
Extended Service Life: Reduced frequency of repairs and replacements.
-
Lower Environmental Impact: Improved recyclability and reduced need for chemical treatments.
-
Enhanced Safety: More resilient structures that can better withstand harsh conditions.
Conclusion
Corrosion poses a significant challenge to steel fixing structures in solar panel installations, impacting both safety and cost-effectiveness. By exploring and adopting alternative materials—such as stainless steel, aluminum, or composite materials—industry professionals can mitigate these risks while enhancing sustainability and long-term performance.
As the renewable energy sector continues to grow, investing in corrosion-resistant solutions will be key to maintaining reliable and efficient solar installations. In our next article, we delve into one such innovative approach: FRP lamination as a corrosion barrier for solar panel structures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is steel prone to corrosion in solar panel structures?
Steel corrodes when exposed to moisture, salt, and temperature fluctuations, leading to structural degradation and increased maintenance needs.
What are the main alternatives to steel for solar panel fixing structures?
Alternatives include stainless steel for enhanced corrosion resistance, aluminum for lightweight applications, and composite materials for high durability and low maintenance.
How do alternative materials improve sustainability?
They often offer longer service life, require less maintenance, and reduce the overall environmental impact through better recyclability and resource efficiency.
#solarpanelstructures #steelcorrosion #corrosionchallenges #alternativematerials #stainlesssteel #aluminum #compositematerials #renewableenergyinfrastructure
Disclaimer:-
The content on this site is for general information and entertainment purposes and does not constitute legal counsel. We strive to keep our information as accurate as possible. However, we make no warranties about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the information contained on this page. You should rely on this information at your own risk. This website may include links to other third-party sites. These links are provided as a convenience to you as a reader, user, or browser only. We make no representation, warranty, or guarantee, nor do we endorse or take responsibility for any of the content of such sites.
Stay in touch with us if you’re interested in hearing from us promptly.
- Website - https://www.muifatt.com.my/home/
- Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/muifattmarketing
- Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/muifattmarketing/
- Google - https://goo.gl/maps/WxVY13gNcaRTS7Jp6
- Youtube - http://www.youtube.com/@MuiFattMarketing
- TikTok - https://www.tiktok.com/@muifattmarketing
- LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/mui-fatt-marketing-sdn-bhd-
- Linktree - https://linktr.ee/muifattmarketing
- Shopee - https://www.shopee.com.my/muifattmarketing
- Lazada - https://www.lazada.com.my/shop/mui-fatt-marketing
Recent Blog
The Ultimate Guide to Locking Mechanisms for FRP Molded Grating
Understanding the right locking method for FRP molded grating is crucial for safety and durability. Learn about M clips, J clips, C clips, and disk plates, along with installation recommendations to ensure a secure and stable grating system.
Enhancing Solar Panel Fixing Structures with FRP Lamination: A Corrosion Barrier Solution
An expert look at how FRP lamination acts as a corrosion barrier for solar panel fixing structures, offering advanced protection and sustainability benefits.
The Essential Guide to Kickplates: Safety, Style & Compliance
Learn why kickplates matter for safety, style, and compliance. Discover how they improve accessibility and meet building code requirements.
Essential Guidelines for Water & Septic Tanks in Borneo
Understand the regulations and guidelines for water and septic tanks in Borneo, plus compliance with SPAN, IWK, and SIRIM standards in Malaysia.
The Costly Mistake of Using Unsuitable Resin for FRP Tanks
Explore the risks of unsuitable resins for FRP wastewater tanks, including a real-life example of NaOH corrosion. Learn how to avoid costly failures.
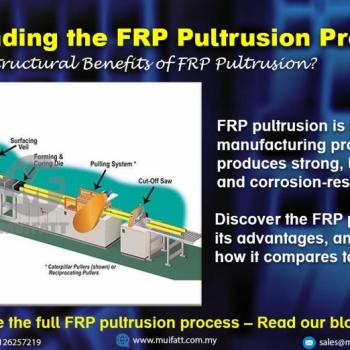
Mastering the FRP Hand Lay-Up Process: Methods, Benefits, Sustainability
Discover the FRP hand lay-up manufacturing process, its importance, differences from other methods, and how it aligns with your custom project needs.
Transform DIY Projects with FRP Pultruded Profiles
Explore the versatility of FRP pultruded profiles and how they can elevate your DIY landscaping projects. Get inspired by Mui Fatt's successful applications and learn how to create custom solutions for small- to larger-scale projects.